organizational structure: hierarchy of business organizational chart: diagram of structure.
Terms
- Delegation advantages
- motivate employees
- improve quality and speed of decision making. no need for senior managers
- reduce workload on senior managers
- improves skills and qualities of employees limitations
- additional pay, more costs for business
- got to invest in training of employees
- does not motivate everyone, not everyone wants to be accountable
- some people don’t want to do manager work
- decision making is best for senior executives
- Span of control
- how many workers are accountable for a line manager
- managers with narrow span of control have tighter control over decision making
- Wide span of control: manager has responsibility for many subordinates
- Three factors that decide to adopt a wide or narrow span of control
- employee competencies
- managerial competencies
- business context
- levels of hierarchy
- tall structure: large number of levels of hierarchy
- flat structure: few layers spread wide (fast communication)
- chain of command
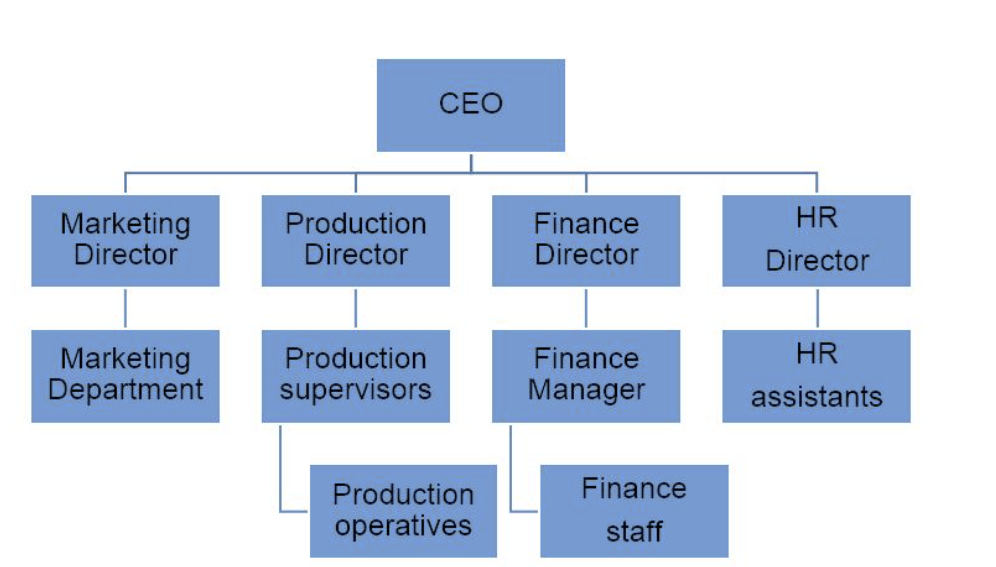
- bigger businesses have taller chain of commands
- bureaucracy
- administrative systems within an organization
- lots of paperwork to get tasks approved
- large well established organizations are bureaucratic
- centralization
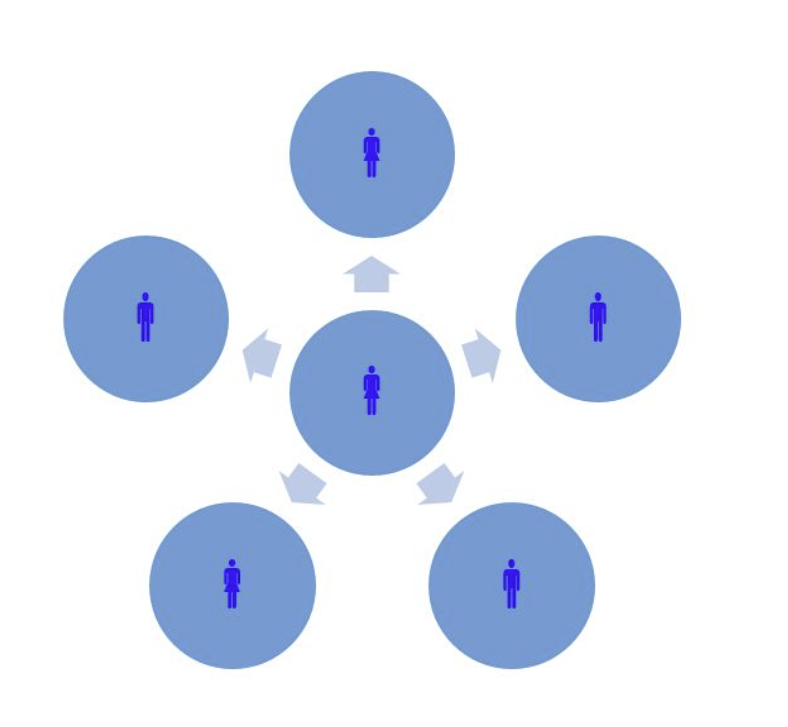
- only a few people are involved with decision making. everyone reports to them. Rarely any delegation.
- Good when: you need to make decisions fast, your workforce is unskilled, cost savings
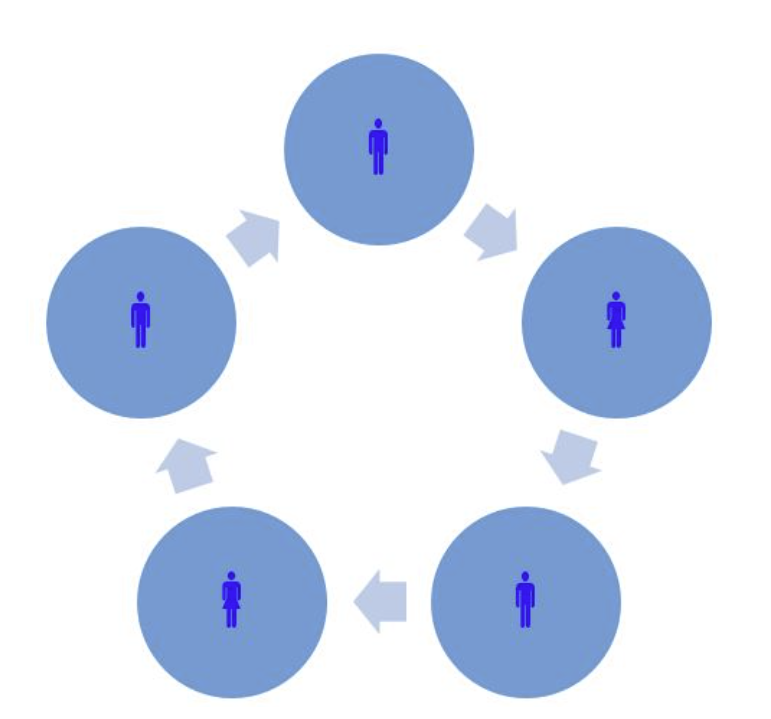
- decentralization
- decentralization throughout the organization
- tend to have flatter and wider spans of control
- improve morale and productivity
- decision making is flexible and quick
- de-layering
- remove layers in a hierarchical structure
- do this to cut costs and remove bureaucracy
- matrix structure
- based on needs of business
- matrix structure organize individuals multiple roles, multiple reporting lines
- task oriented. allows firms to be responsive to market demand
- use experts to generate new ideas, improve productivity
- isolate team members outside of their departments
- conflicts between managers and employees
