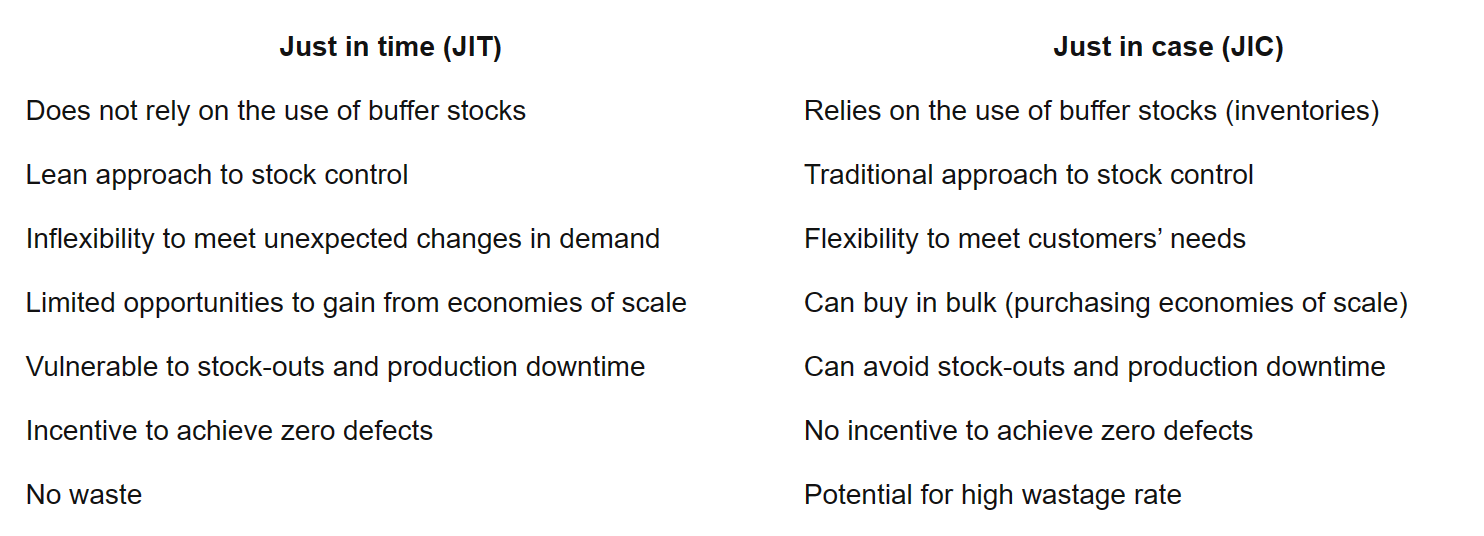
JIT
- lean production method of stock control
- deliveries of stock just in time for them to be used in production process
- removes cost of buffer stocks
- eliminates storage, reduces insurance, and maintenance
- continuous improvement, difficult to manage for big organizations
- stock is delivered right after required for production
- working capital is not tied up in inventory, which might not be liquid
STORAGE COSTS
- storage
- insurance
- wastage
- security (for theft prevention)
- maintenance
- damage
advantages
- no buffer stocks
- minimal wastage
- improve liquidity
- improve competitiveness due to lower costs of stock management + improved product quality disadvantages
- harder to get economies of scale
- tech to manage stock is expensive
- relies on 3rd parties
- inflexible if demand increases suddenly
JIC
- have buffer stocks so you always have enough in case of changing demand
- meet unexpected orders quickly
- suitable for durables, not perishables
- power tools, batteries, torches, nails, pens, greeting cards, lego toys, toothpicks advantages
- buffer stocks are flexible for sudden changes in demand
- production can continue even if suppliers give stock late (because of buffer stock)
- economies of scale when you buy stuff in bulk
- customers don’t have to wait for product disadvantages
- costs ⇒ insurance and maintenance + security of stocks
- subject to damage or theft
- stockpiling reduces cash flow + working capital
- suppliers can charge high prices for urgent deliveries of stock
- unsuitable for perishable products (i.e. food)