- product
- price
- promotion
- place
- people
- processes
- physical evidence
- appropriateness of marketing mix
marketing mix
- set of decisions that need to be made by managers
- Goods: 4 Ps product price promotion place
- Services 7 Ps - + processes, physical evidence, people
product
FMCG - fast moving consumer goods (toothbrush, no expiration but is used up quickly). durables - last a long time. speciality goods - unique and limited distribution channels (i.e. designer clothes)
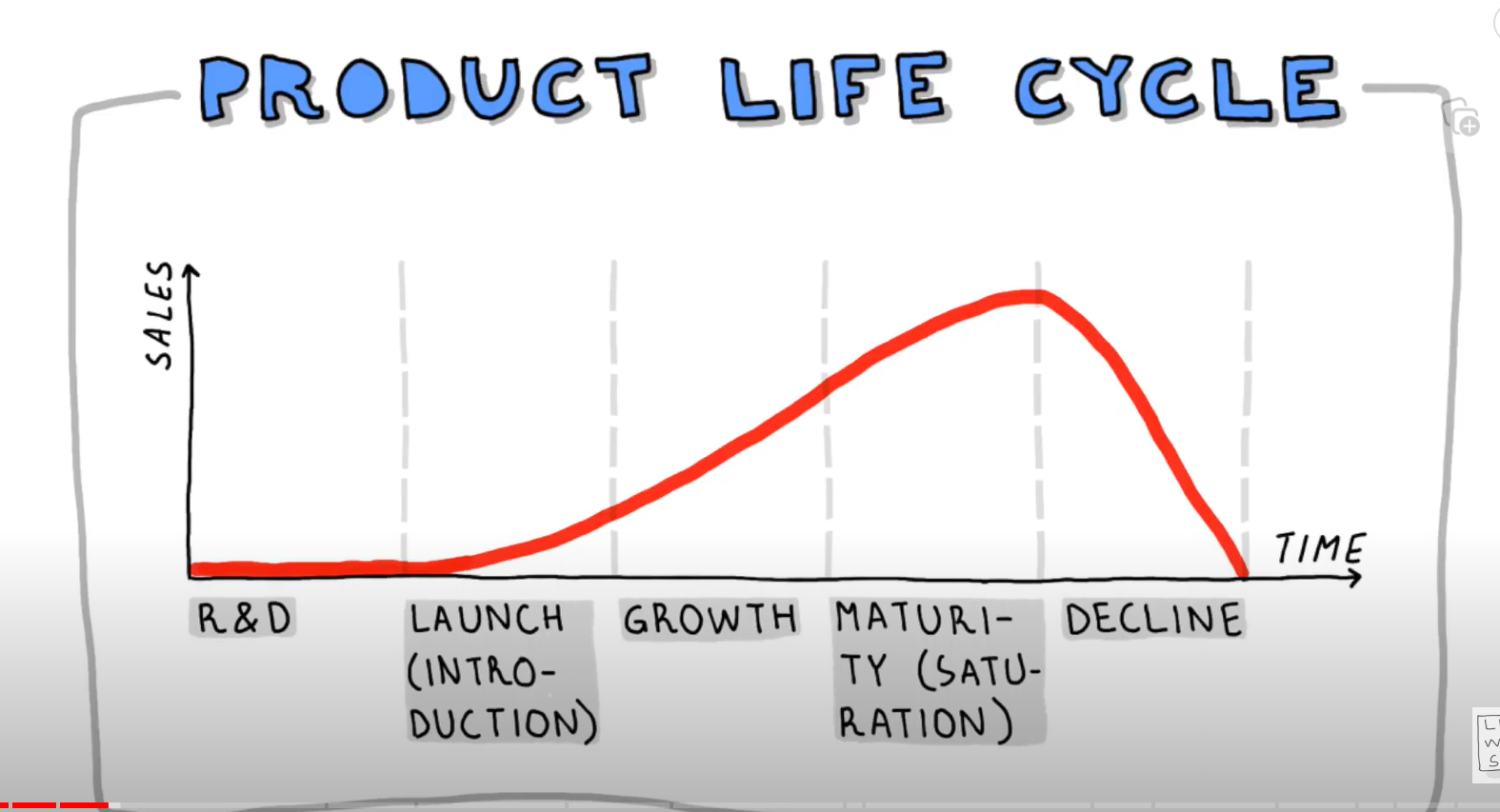
product lifecycle
- stages a product goes through from launch to decline product portfolio
- menu of organization
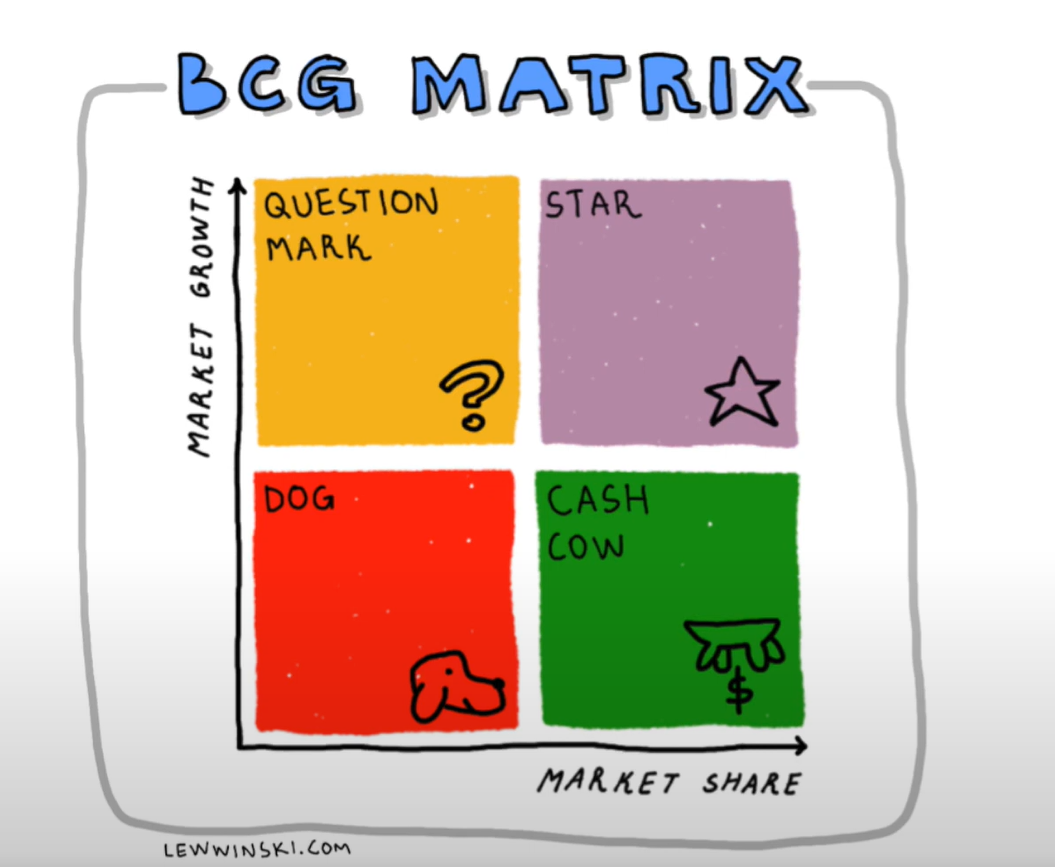
- product portfolio analysis ⇒ use BCG matrix

| Syntax | Description |
|---|---|
| Header | Title |
| Paragraph | Text |
stages R&D (only cash outflows) launch(star or question mark) growth maturity decline
Product extension strategies
- plan to avoid decline/prolong maturity
- Market development (ansoff matrix) (new markets to sell too)
- redesigning product (“limited edition”)
- targeting new segmetns (new people to sell the same product, different customer groups)
- price reductions
- repackaging
- differentiation ( USP )
- SLAP (effect on stakeholders, long term effect, advantages, disadvantages)
Branding - combination
 brand: how a company wants to be recognized
aspects of a company’s brand - be recognizable, improve awareness, get customer dedication, premium that the customers are willing to pay for the product
brand development - strengthen the brand (improve awareness). generic brand (xerox, kleenex)
brand loyalty - buying the same product over and over again
brand: how a company wants to be recognized
aspects of a company’s brand - be recognizable, improve awareness, get customer dedication, premium that the customers are willing to pay for the product
brand development - strengthen the brand (improve awareness). generic brand (xerox, kleenex)
brand loyalty - buying the same product over and over again
- positive WoM (word of mouth), celebrities brand value - how much customers are willing to pay above the value of the product (acts as an entry barrier)
importance of branding
- copyright (legal protection)
- differention strategy
- adds values
- increases profit margins
- customer loyalty

price
pricing strategies
- cost plus average cost + markup
- penetration charge really low prices to attract customers increase sales and awareness low profitability and brand value (cheap, low quality products)
- loss leader sell certain products as a loss
- attract potential customers, works well for FMCG, causes brand switching
- works only if customers purchase other products too, otherwise you’re in loss (disadvantage)
- predatory DANGEROUS PRICE WARS AHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH work short term
- increased market share, and high entry barrier
- can result in a MONOPOLYYYYYYY bads
- not sustainable long term, unethical/illegal
- profitability is at a risk
- premium
- setting a high price for premium high quality products advantages - high margins, good brand value
- low sales value, does not apply to every product (con)
- dynamic
- price changes based on circumstance
- adv: flexibilyt, chance to maximze profits (i.e. gas prices)
- dis: not applicalble to many products (can cause customer dissatisfaction (i.e. high price for umbrella when it rains))
- competitive
- lower/increase price product based on compitors
- ensures sales encourgase brand loyalty
- reliance on competitive (i.e. companies may use predatory pricing, bad for you, ) not sustainable long term
- contribution price - AVC
- profitability is ensured, your price is higher than AVC
- disregards competitors price (disadvantage) not offer a competitive price PED
- you change the price, demand chance
- Inelastic (0 - 1), price change does not change demand much
- Unit elastic 1: % change in price equals % change in demand cange
- elastic > 1 (small change in price greatly affects demands) Promotion
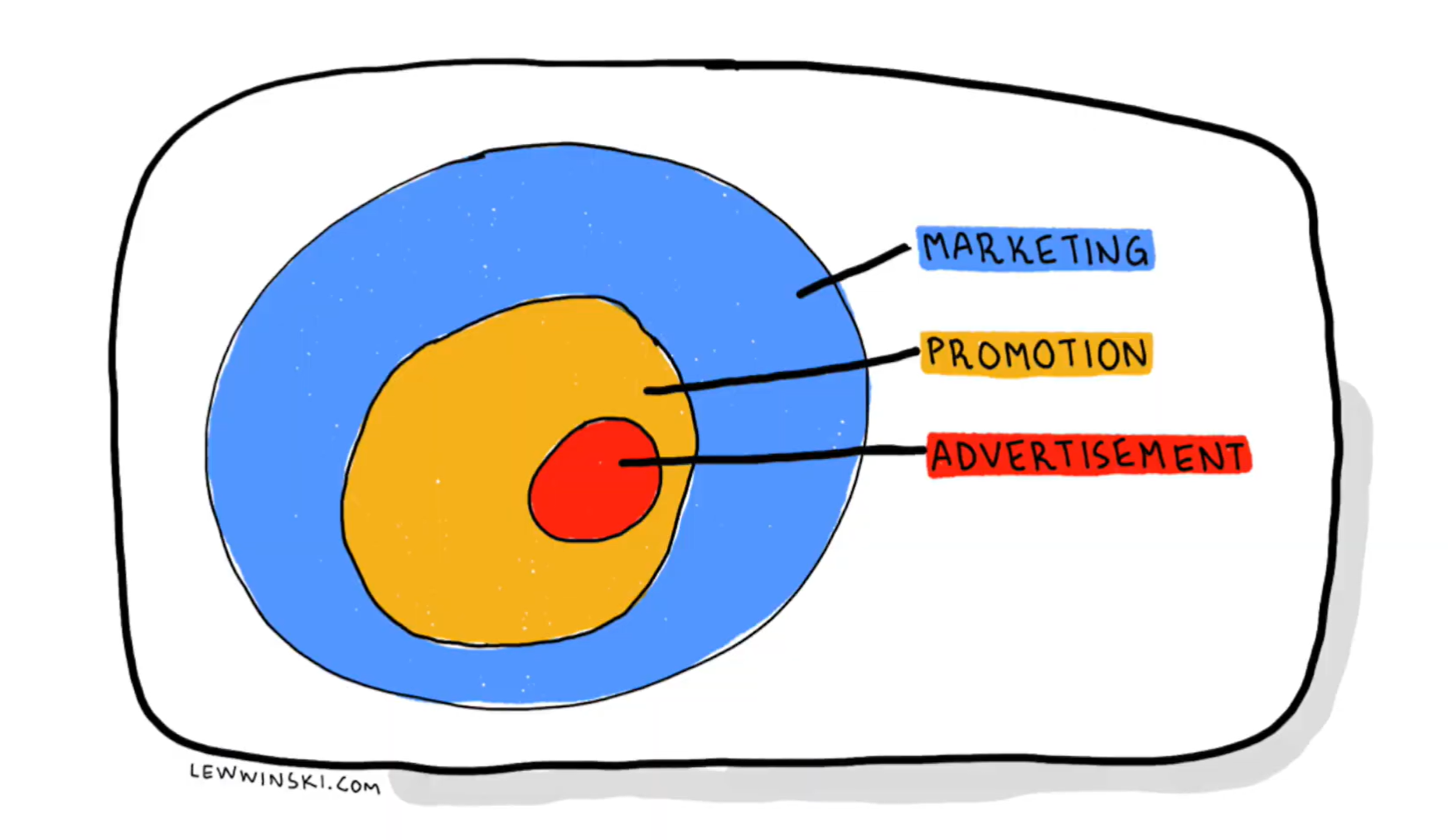
- communicate messages about product/brand to the customers promotional mix: advertising, personal selling, public relations, sales promotions
aspects of promotion
above the line — mass media
below the line - directed, not mass media
TTL 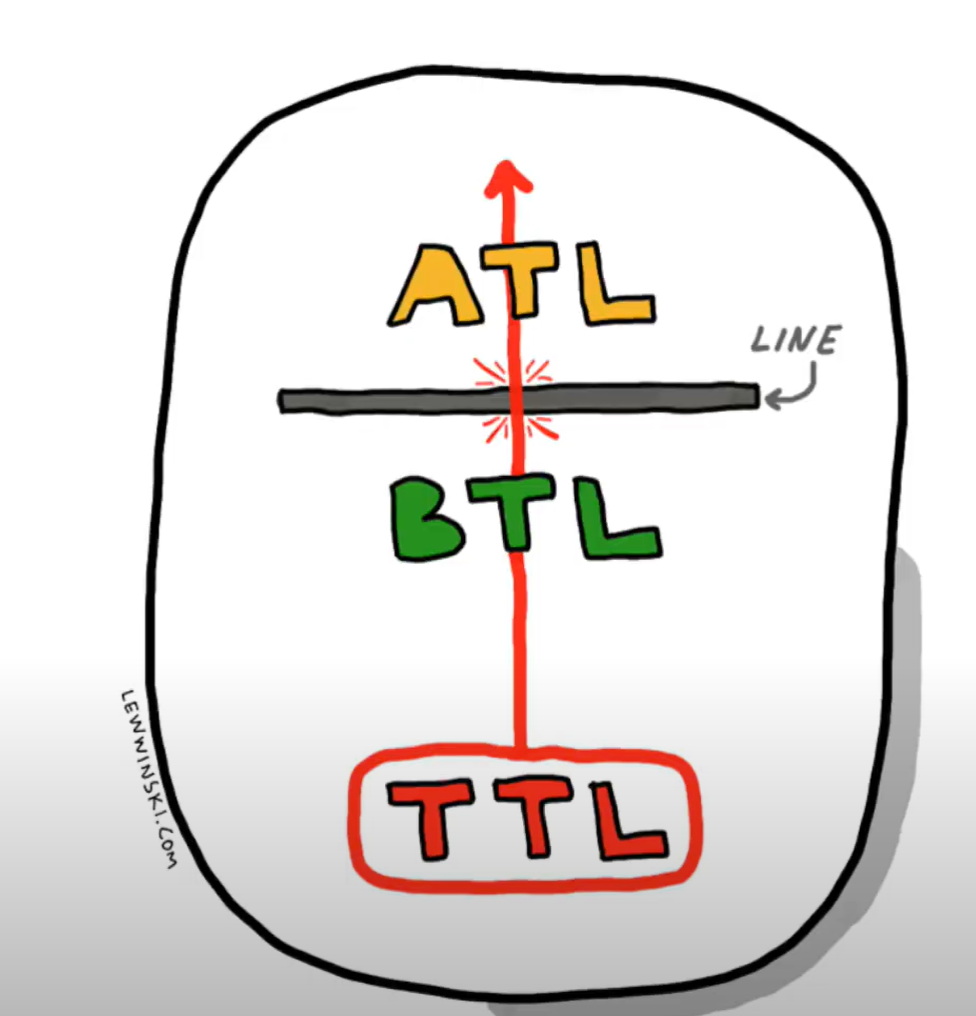 Through the line : ATL + BTL
Through the line : ATL + BTL
ATL
- mass media
- targeting
- increases awareness
- reaches a wide audience
- expensive BTL
- non mass media
- targeted
- secures sales
- reaches a small audience
- relatively cheap
promotional mix - advertising, pr, personal selling sales promotion
advertising: informative (understand benefits of a product, appeals to logic) + persuasive
 - comparative advertising, numerical factor (informative factor, throwing stats at you)
- persuasive advertisement: appeals to emotion (celebrity endorsement, feel good factor, bargain appeals, slogans)
- comparative advertising, numerical factor (informative factor, throwing stats at you)
- persuasive advertisement: appeals to emotion (celebrity endorsement, feel good factor, bargain appeals, slogans)
- personal selling (i.e. car dealership, person-to-person sales/purchasing experience)
- PR - promotional activities aimed at increasing brand value, reposition a brand/product “there is no such thing as negative publicity”
- sales promotion: encourage sales of a product (buy one get one free, free gifts)
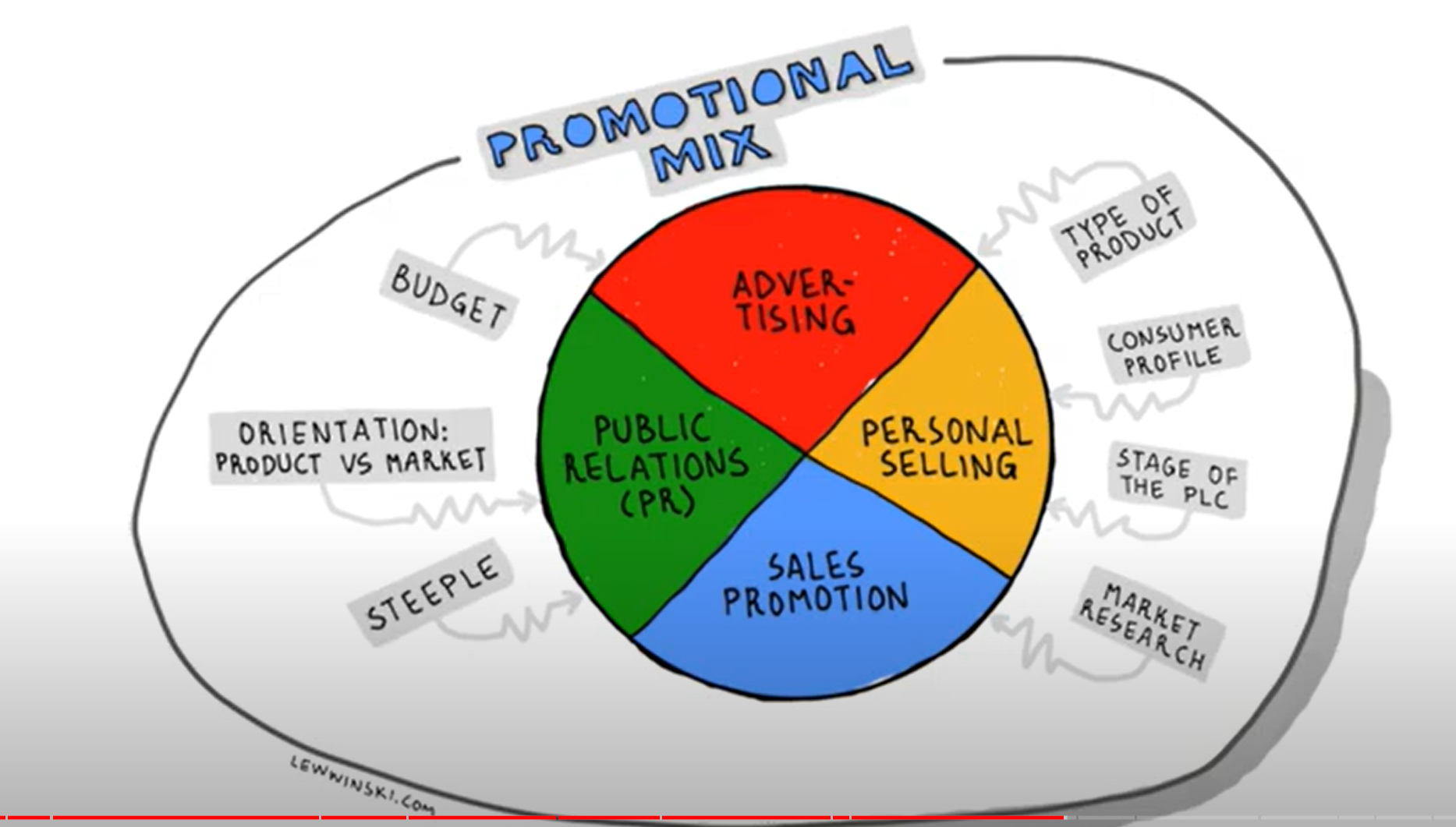 APPS - advertising PR personal selling sales promotion
APPS - advertising PR personal selling sales promotion
ATL media - tv radio newspaper magazine outdoor advertising BTL - POS, direct mail, publicity through brand ambassadors, WoM, events TTL: digital marketing (SMM - social media marketing) SMM - clear KPIs and metrics (direct response, cost efficiency, improved brand awareness), complementary to traditional marketing
Places (better name is distribution)
- about distribution channels
- how product gets to consumer
- getting the right product to the right people at the right time at the right place
- intermediaries link in distribution
- retailers
- distributors
- agents
- wholesalers (retailer that buys/sells in bulk)
- car dealerships
- vending machines
- zero level
- sold directly to consumers
- got to deal with logistics
- smaller lowerhead cost
- one level
- retailers, distributors, agents, car dealerships
- retailers in charge of distribution storage and sales
- you got to be reliant on someone, and they take a slice out of your product
- retailers, distributors, agents, car dealerships
- two level
- works well when you are far away from your customers
- wide coverage of locations, sales revenues in large quantities in a short time
- lower profit margins and even higher profits
(next three apply to services only) people
- the people selling your services
- essential to decision for services
- not all services involve humans (i.e. AI), cashierless supermarkets
- culture - employee - consumer relations
- cultural gap (think globally, act locally) monoculture environment : easy to sell, no diversity
- multicultural gap (having to adapt, diversity) processes
- concerned with the purchasing experience
- how the sale is made
- delivery, customer service, payment methods, waiting/queueing times

physical evidence
- tangible aspects of a service
- allows customers to evaluate and predict the quality of provided services
- i.e. rating systems (private school furniture, class sizes, equipment)
